If you’ve already been following our accessibility in design series, you’ll know that we’ve so far covered colour testing, typography and legibility. And if you’re new here; welcome.
This time round, we’re chatting about the impact of UI states, spacing and sizing on accessibility. As many as 20% of audiences worldwide require some kind of accessibility in the digital world – and so we’ll talk you through how we make sure our UI elements meet the W3C’s minimum AA standards.
Here goes.
Why are sizing, spacing and states important for accessibility?
Short answer: all three are key to usability. The spacing, sizing and overall alignment of your UI elements play a huge part in how your users interact with elements and differentiate between page content.
What are UI states?
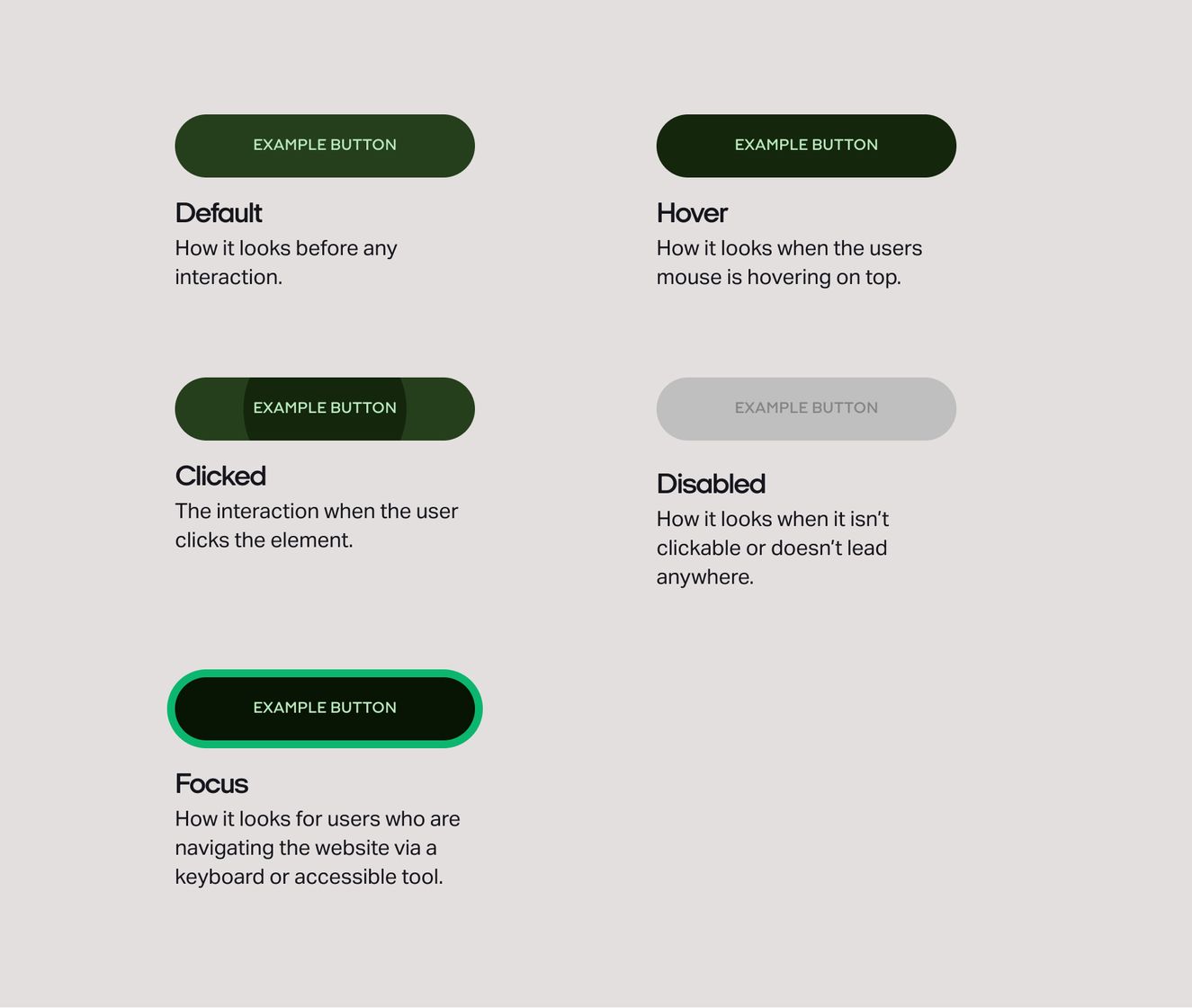
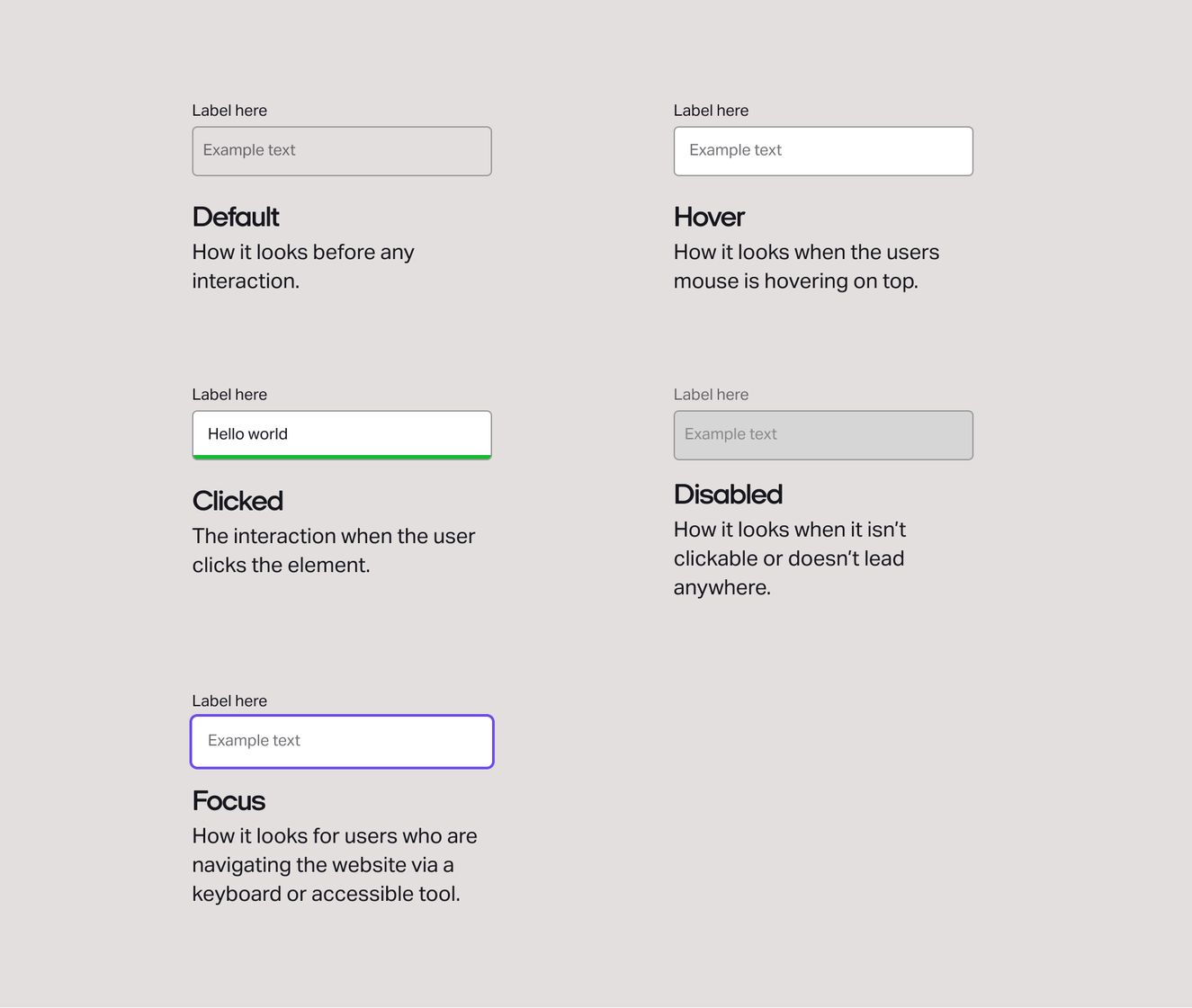
States are the visual representations we use to communicate the status of a component or interactive element.
States allows all users to navigate through your website without the use of a mouse and only a keyboard. If you’ve ever tabbed your way through a website, the visual representation you see to demonstrate the element you are on is a focus state.
And when it comes to accessibility, you may have users that simply don’t have access to a mouse – or, you could have audiences that aren’t able to use a mouse at all. That’s why states matter.
Here are some examples of elements and their states.
Button states
Input fields
Carousel controls

Filters and lists

Sizing and spacing your UI
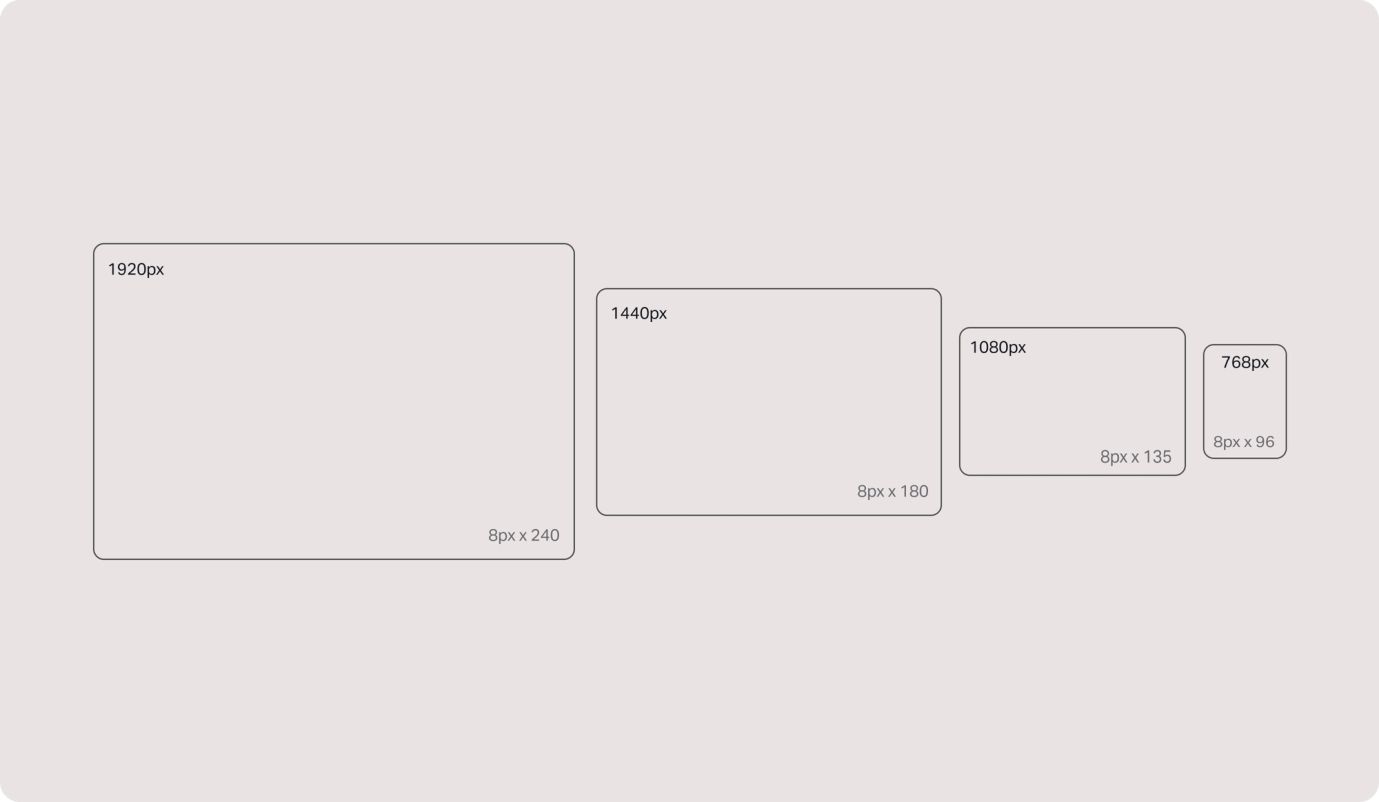
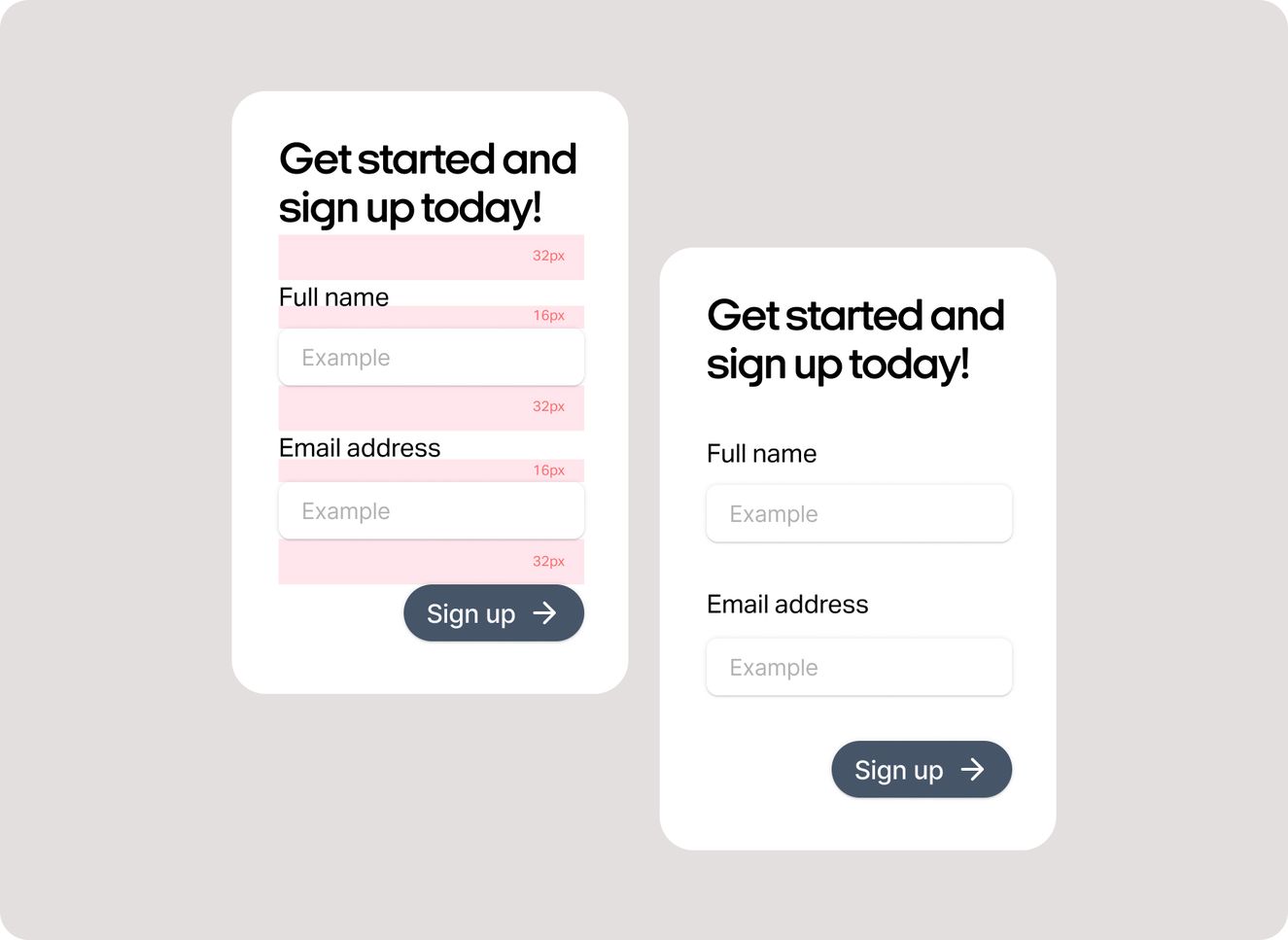
The 8px grid system
The holy grail of grid systems. In web design, the sizing and spacing of every UI element should be in increments of 8px. Why? Because not only will your designs convert seamlessly to rems (for development), but it makes designing for different screen sizes super simple. Every viewport is an increment of 8px, so every element within a page follows the same rule and gives you the best responsive results.
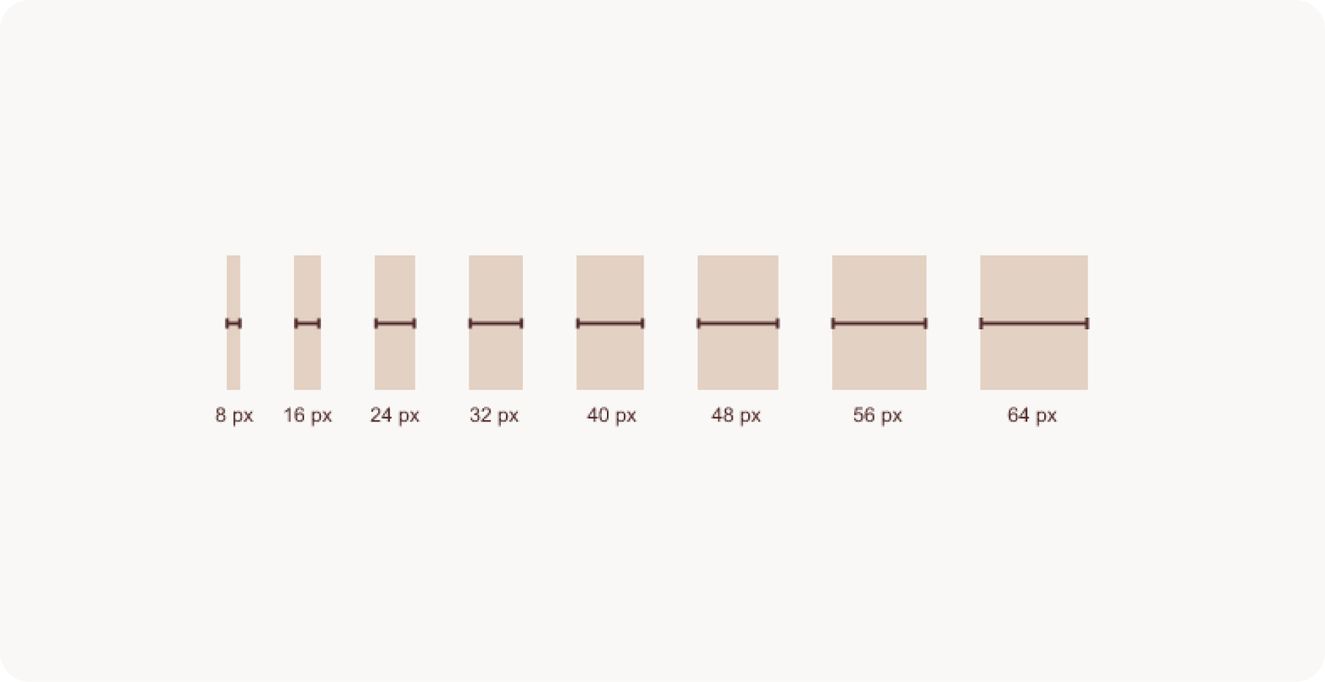
Spacing 101
A couple of tips when it comes to spacing.
It’s important to make sure all of your UI elements that follow the 8px grid system have enough spacing so that accessible users can clearly differentiate and identify content.
Between 24-40px is a good range of padding to have within your containers or spacing between elements so that they are visually different to users with visual impairments.
Sizing 101
And when it comes to sizing…
All of your interactive elements should be accessible to see, click or touch.
As a general rule, these elements should be no smaller in width or height than 40px – the average size of a touch point on touch screen device, and therefore the size that’s most finger-friendly.

That’s it for UI spacing, sizing and states. Next up in our accessibility in design series: how to tackle content hierarchy.


